What Are the 3 P’s of Sustainability?
Sustainability has become more than just a corporate buzzword – it’s a blueprint for how we live, work, and grow. One of the clearest ways to understand this is through the 3 P’s of Sustainability. This framework helps organisations and individuals strike a balance between environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and financial viability. In this article, we’ll explore what the 3 P’s of Sustainability are, why they matter, and how you can apply them in real life.
Understanding the 3 P’s of Sustainability
The 3 P’s of Sustainability stand for People, Planet, and Profit. Sometimes called the triple bottom line, this model helps businesses and governments measure success beyond mere financial results. You may also hear it referred to as the three ps of sustainability or even the three pillars of sustainability, but all these terms point to the same idea: sustainable systems must meet social, environmental, and economic needs together.
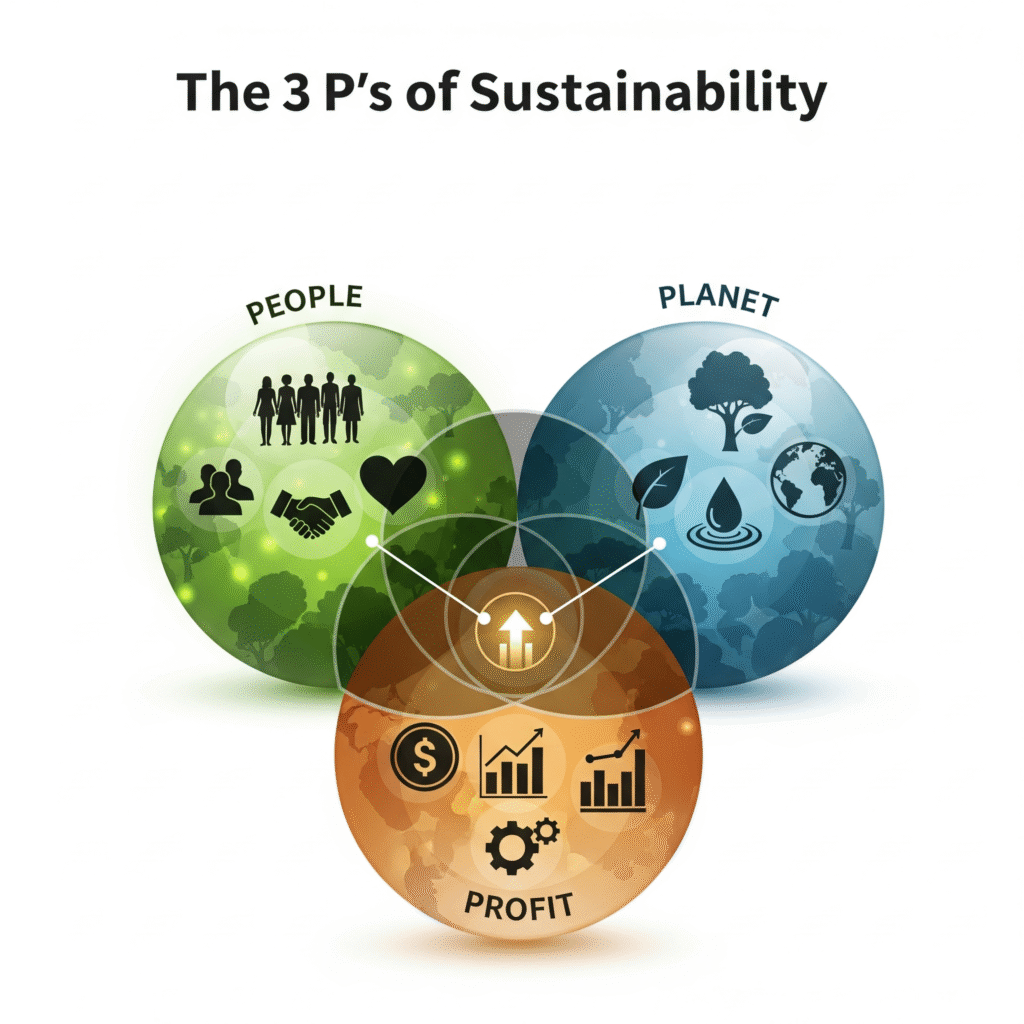
This framework emphasises that growth today should not compromise future generations. It combines eco-friendly practices, social equity, and long-term profitability into one balanced approach.
The First P: People
The first pillar focuses on People – the social aspect of sustainability. It is about how organisations affect communities, workers, and society at large. Companies that value people commit to fair wages, safe working conditions, ethical sourcing, and community development.
Examples of “People” practices include:
- Supporting local suppliers to strengthen communities
- Ensuring fair labour standards across the supply chain
- Promoting diversity and inclusion in the workplace
- Providing training and awareness about sustainable living
When businesses put people first, they build trust, loyalty, and a positive reputation. This not only benefits society but also enhances long-term success.
The Second P: Planet
The second “P” stands for Planet, which represents the environmental pillar of sustainability. This is about protecting natural resources and reducing harm to the environment. Businesses are expected to cut their carbon footprint, conserve water and energy, and adopt materials with lower environmental impact.
Practical actions under “Planet” include:
- Using biodegradable packaging instead of single-use plastics
- Switching to renewable energy sources
- Implementing waste reduction and recycling programmes
- Designing products with a circular economy approach
For example, companies like GreenMatter Packaging develop eco-friendly packaging solutions that help businesses reduce plastic waste. By taking care of the planet, organisations also meet rising consumer demand for sustainable products and stay ahead of tightening environmental regulations.
The Third P: Profit
The third “P” is Profit, which reflects the economic dimension of sustainability. Profit ensures that organisations can survive and reinvest in sustainable practices. This isn’t about chasing quick wins – it’s about creating enduring value for stakeholders.
Benefits of focusing on profit within a sustainable framework include:
- Savings from energy efficiency and waste reduction
- Competitive advantage with green products
- Enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty
- Long-term financial resilience
When businesses demonstrate that sustainability can also be profitable, they inspire wider adoption and innovation. Profit turns sustainability from an obligation into an opportunity.
Why the 3 P’s of Sustainability Matter
The 3 P’s of Sustainability provide a simple but powerful roadmap for balancing social, environmental, and financial priorities. By integrating People, Planet, and Profit, organisations can:
- Meet growing consumer expectations for eco-conscious products
- Comply with environmental and labour regulations
- Attract investors and partners who value ethics
- Contribute to a healthier society and ecosystem
The 3 ps of sustainability also encourage a shift away from the traditional “take-make-dispose” model toward one that values reuse, recycling, and regeneration. This approach is essential for building resilience in today’s economy.
Putting the 3 P’s Into Action
Applying the 3 P’s of Sustainability is not just for large corporations. Small businesses and individuals can also integrate these principles into everyday decisions. Some practical steps include:
- Choosing biodegradable bags and compostable packaging over conventional plastics
- Partnering with ethical and local suppliers
- Educating customers about responsible consumption and disposal
- Tracking environmental and social impact metrics for transparency
These actions not only protect the environment but also strengthen brand loyalty and reduce operational risks.
The Broader Impact
When organisations embrace the three ps of sustainability, they go beyond improving their own bottom line. They help create a future where economic activity, community wellbeing, and environmental stewardship coexist. This is the essence of the three pillars of sustainability – systems that are environmentally sound, socially fair, and economically viable.
Conclusion
The 3 P’s of Sustainability – People, Planet, and Profit – offer a clear, actionable framework for making choices that drive positive change. Whether you’re a business owner, policymaker, or individual consumer, understanding and applying this model empowers you to contribute to a greener, fairer future.
By embedding these principles into decision-making, we move closer to a world where products, services, and lifestyles are truly sustainable – benefiting not only today’s stakeholders but generations to come.


